AlphaEarth Foundations: AI-Powered Planetary Mapping at Unprecedented Scale 🌍
AlphaEarth Foundations, developed by DeepMind, is a breakthrough AI model that integrates petabytes of multimodal Earth observation data to generate unified digital representations of terrestrial land and coastal waters. This “virtual satellite” enables consistent, high-resolution mapping and monitoring of the planet, overcoming longstanding challenges of fragmented datasets and limited satellite coverage. By compressing vast data into compact embeddings—requiring 16 times less storage than previous systems—AlphaEarth Foundations allows for rapid, large-scale analysis and detailed tracking of environmental changes. The model underpins the new Satellite Embedding dataset now available in Google Earth Engine, which is already being leveraged by over 50 organizations globally to classify ecosystems, monitor agricultural changes, and enhance conservation efforts. With superior accuracy (24% lower error rates than comparable models) and robust performance even with limited label data, AlphaEarth Foundations sets a new standard for geospatial intelligence. Its integration with broader AI agents, like Gemini, signals a future of even more powerful, automated environmental insights for research, policy, and industry.
Key Points
- AlphaEarth Foundations unifies diverse Earth observation data into a single, highly efficient digital embedding for each 10x10m land or water square.
- The model drastically reduces storage and computational costs, enabling planetary-scale mapping with 16x smaller data summaries than prior AI systems.
- Outperforms traditional and AI-based mapping solutions, delivering 24% lower error rates and excelling even with sparse label data.
- The Satellite Embedding dataset, powered by AlphaEarth, is driving real-world applications for ecosystem classification, agricultural monitoring, and conservation planning across global organizations.
- Future integration with general reasoning LLMs like Gemini is expected to further enhance automated, actionable environmental insights.
# ChatGPT Study Mode: AI’s Socratic Shift in Education 🚀
OpenAI has introduced a new “study mode” for ChatGPT, targeting students who might otherwise use the AI tool for quick homework answers. This feature, built on the Socratic method, guides users with open-ended questions rather than supplying direct solutions. While the intent is to foster deeper engagement and understanding, the underlying challenge remains: students can easily toggle back to the standard mode for direct answers. OpenAI claims that using ChatGPT as a tutor, rather than an answer machine, improves learning outcomes, and is partnering with Stanford to study AI’s impact in K-12 education. Despite these efforts, concerns persist about long-term over-reliance on AI and potential erosion of critical thinking skills. The company is positioning study mode as a way to encourage genuine learning, but the temptation for shortcuts is just a click away—raising questions about how AI will reshape educational habits and outcomes.
Key Points:
- ChatGPT’s new study mode uses the Socratic method to encourage active learning and discourage shortcut-seeking.
- The feature is available to most users, including those on the free version, and targets both university and K-12 students.
- OpenAI is partnering with Stanford to research AI’s impact on learning outcomes.
- There are ongoing concerns about students’ potential over-reliance on AI, which could hinder critical thinking.
- The ease of switching between study and standard modes means the risk of bypassing deep learning remains.
Apple Unveils Advanced AI Model Architecture and Training Insights 🚀
Apple has released a detailed technical report on its new foundation AI models, offering a rare look into the architecture, training processes, and data strategies powering Apple Intelligence in iOS 18 and beyond. The report outlines significant advances in both on-device and cloud-based models, emphasizing efficiency, scalability, and privacy. Notably, Apple’s on-device model is split into two blocks to optimize memory and speed without sacrificing performance. The cloud model introduces a Parallel-Track Mixture-of-Experts (PT-MoE) architecture, enabling faster, more accurate responses by activating specialized subnetworks as needed. Apple also reports a 275% increase in multilingual representation, expanding support for non-English languages through improved data sourcing and tokenizer enhancements. Data for training was sourced from public web content, licensed material, synthetic data, and over 10 billion image-caption pairs, with a strong focus on privacy and content quality. This technical transparency signals Apple’s commitment to closing the AI gap while maintaining its reputation for privacy and device-centric intelligence.
Key Points - On-device model split into two blocks, reducing memory usage and latency by 37.5% while preserving output quality. - Cloud-based model uses a Parallel-Track Mixture-of-Experts (PT-MoE) architecture for modular, efficient, and scalable AI processing. - Multilingual data in training increased from 8% to 30%, with tokenizer size expanded by 50% to 150K tokens. - Training data sources include public web, licensed content, synthetic data, and over 10 billion image-caption pairs. - Apple maintains a privacy-first approach, filtering low-quality data and respecting web crawler exclusion protocols.
ChatGPT Surges to 2.5 Billion Daily Prompts: AI Usage Growth Rivals Search Giants 🚀
OpenAI’s ChatGPT has reached a significant milestone, now handling over 2.5 billion user prompts every day, with 330 million of those originating from the US. This explosive growth highlights ChatGPT’s rapid adoption and its emerging position as a formidable competitor to established search engines. According to data confirmed by OpenAI and reported by Axios, ChatGPT processes more than 912.5 billion requests annually. While Google still leads with 5 trillion annual searches, the pace at which ChatGPT is gaining traction is noteworthy. In just a few months, its weekly user base jumped from 300 million in December to over 500 million by March. This trend underscores the accelerating shift in user behavior toward AI-driven platforms for information retrieval, productivity, and problem-solving. For technical leaders and product strategists, these figures signal a paradigm shift in digital engagement, suggesting that AI chatbots are not only supplementing but potentially redefining the way users interact with technology and access information. Key Points
- ChatGPT now processes over 2.5 billion prompts daily, totaling 912.5 billion annually.
- 330 million daily requests come from US-based users.
- User base surged from 300 million weekly in December to 500 million in March.
- While Google remains ahead with 5 trillion searches annually, ChatGPT’s growth rate poses a real challenge.
- The data highlights a major shift toward AI-driven information retrieval and digital engagement.
AWS Unveils Kiro: Specification-Driven Agentic IDE for Enterprise-Grade AI Coding 🚀
AWS has launched Kiro, a specification-driven integrated development environment (IDE) designed to bring rigor and structure to AI-assisted software development. Unlike earlier “vibe coding” tools that quickly translate natural language prompts into code, Kiro focuses on transforming those prompts into comprehensive specifications, technical designs, and implementation plans. Built on the open-source Code OSS foundation, Kiro integrates leading AI models (Claude Sonnet 4.0 and 3.7) and introduces a two-tier architecture with automated hooks for quality assurance and security. The platform operates independently from AWS’s cloud ecosystem, offering a cloud-agnostic, usage-based pricing model tailored to enterprise needs. Kiro aims to address enterprise concerns about governance, compliance, and documentation by maintaining traceable links between requirements, design, and code. Its success will depend on whether it can deliver superior structure, auditability, and code quality compared to existing agentic coding tools, and whether it can ease enterprise adoption barriers such as workflow integration and security governance.
Key Points - Kiro turns natural language prompts into structured specs, design docs, and sequenced implementation tasks. - Built on Code OSS, Kiro integrates Claude Sonnet models and supports event-driven automation for QA and security. - Operates as a standalone, cloud-agnostic IDE with usage-based pricing, departing from AWS’s typical cloud-centric tools. - Focuses on enterprise needs: traceability, audit trails, and synchronized documentation to address compliance and governance. - Seeks to overcome adoption barriers by aligning AI coding workflows with established software development practices.
Hugging Face Faces Scrutiny for Hosting 5,000 Nonconsensual AI Models of Real People 👤
Hugging Face, a leading AI model-sharing platform, is currently hosting over 5,000 AI image generation models that replicate real people’s likenesses—most notably female celebrities—without their consent. These models were previously banned and removed from Civitai, another AI platform, after pressure from payment processors due to their use in creating nonconsensual pornography. Following Civitai’s ban, a coordinated community effort archived and reuploaded these models to Hugging Face, often disguising them with generic names to evade detection. Despite Hugging Face’s stated content policies against unlawful and non-consensual sexual content, there is no explicit ban on models that recreate real people’s likenesses. The company’s own Ethics & Society group advocates for “consentful” technology, but enforcement appears lacking. This raises significant ethical and operational questions for platforms managing open AI model repositories, especially as regulatory and reputational risks mount.
Key Points - Over 5,000 nonconsensual AI models of real people, mostly female celebrities, are hosted on Hugging Face after being banned from Civitai. - A community-driven effort used Discord and automated tools to archive and reupload models, masking their true purpose with generic names. - Hugging Face’s content policy does not explicitly prohibit AI models that replicate real people’s likenesses. - The situation highlights gaps between ethical guidelines and actual enforcement on AI platforms. - Growing scrutiny from payment processors and the public increases reputational and legal risks for platforms hosting such content.
🚀 Claude AI Transforms Financial Services: Next-Gen Analytics, Integration & Security
Anthropic has launched a comprehensive Financial Analysis Solution powered by Claude AI, aimed at revolutionizing how finance professionals analyze markets, conduct research, and make investment decisions. The platform unifies diverse data sources—ranging from market feeds to internal enterprise data—into a single, secure interface with direct source hyperlinks for instant verification. Claude 4 models outperform competitors in financial benchmarks, automate complex modeling, and integrate with leading platforms like Databricks, Snowflake, FactSet, and Morningstar. The solution also offers pre-built connectors, robust code automation, and expert onboarding. Security is paramount: user data is never used for model training, ensuring confidentiality. Early adopters, including Bridgewater, NBIM, Commonwealth Bank of Australia, and AIG, report dramatic productivity gains, improved accuracy, and accelerated workflows. Claude is available via AWS Marketplace, with Google Cloud support coming soon, enabling streamlined enterprise adoption and procurement.
Key Points - Unified platform integrates real-time financial data from leading providers for instant, multi-source verification. - Claude 4 models deliver industry-leading performance in financial analysis, modeling, and automation. - Pre-built connectors and robust code tools support compliance, risk modeling, and proprietary system modernization. - Strong security: data is not used for model training, maintaining strict confidentiality. - Proven enterprise impact with significant productivity and accuracy gains reported by major financial institutions.
Google Gemini AI Summaries Vulnerable to Prompt Injection Attacks 🛡️
A recently discovered vulnerability in Google Gemini’s AI-powered Gmail summaries exposes users to a new breed of phishing attacks. Hackers can exploit Gemini’s summarization feature by embedding invisible text in emails using HTML and CSS. While these hidden messages are not visible to users, Gemini processes them and can summarize malicious instructions as part of its output. One documented attack involved the AI-generated summary warning users of a compromised Gmail password and providing a fraudulent support number. Google has acknowledged the risk but claims no evidence of active exploitation and says it is rolling out further security measures. Security experts recommend filtering out hidden text and monitoring AI outputs for suspicious content. For end users, heightened skepticism toward urgent AI-generated warnings is advised, especially if the summary content doesn’t align with the visible email.
Key Points: - Gemini’s Gmail summarization can be manipulated via invisible text, enabling prompt injection attacks. - Attackers bypass traditional spam filters by avoiding links and attachments, increasing inbox delivery rates. - Malicious summaries may include urgent warnings and fake support numbers, mimicking official Google alerts. - Google is enhancing defenses against such attacks but recommends vigilance. - Security teams should filter hidden text and flag summaries with suspicious elements.
California Deploys Generative AI for Power Outage Management ⚡
California is set to become the first US state to leverage generative AI for managing power grid outages, marking a significant milestone in utility tech modernization. The California Independent System Operator (CAISO) will pilot Genie, an AI software from OATI, to automate and optimize real-time outage analysis. Traditionally, CAISO engineers manually scan outage reports and enter data into the grid system—a process that is both time-consuming and fragmented across departments. Genie uses generative AI to consolidate keyword scans, generate proactive reports, and potentially automate decision-making for grid operations. If successful, this could pave the way for broader automation and integration of AI across the grid, enhancing efficiency, reliability, and resilience. Other grid operators, including PJM and ERCOT, are also exploring AI solutions, while international examples like Australia show how AI-driven automation can optimize distributed energy resources. As AI’s role in the energy sector expands, the focus is shifting from managing AI’s energy demands to harnessing its potential to modernize and fortify grid infrastructure.
Key Points: • California’s CAISO to pilot Genie, a generative AI tool, for real-time power outage management. • Genie automates outage report analysis, replacing manual, labor-intensive processes. • Broader adoption could enable autonomous grid operations and improved data-driven decision-making. • Other US grid operators and Australia are advancing similar AI-driven grid modernization initiatives. • The shift signals a new era where AI not only consumes energy but actively strengthens grid resilience and operations.
AWS Launches AI Agent Marketplace with Anthropic Partnership 🤖
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is set to unveil an AI agent marketplace at the AWS Summit in New York City on July 15, with Anthropic as a key launch partner. This new platform will allow startups to directly offer AI agents to AWS customers, streamlining access and deployment for enterprises. AI agents—autonomous software programs leveraging backend AI models—are rapidly gaining traction, but distribution has been fragmented, with most companies operating in silos. AWS aims to centralize and simplify the process, enabling customers to browse, install, and purchase AI agents from various providers in one place. Anthropic, already backed by Amazon and potentially receiving further investment, stands to benefit by expanding its reach and attracting more developers to its API. The marketplace will operate on a revenue-sharing model, similar to SaaS pricing, and is expected to open new revenue streams for startups. AWS joins Google Cloud and Microsoft, who have recently launched similar agent marketplaces, highlighting a broader industry shift toward platform-driven AI agent ecosystems.
Key Points - AWS will launch an AI agent marketplace on July 15, partnering with Anthropic. - The marketplace enables startups to sell AI agents directly to AWS customers. - Anthropic’s involvement may attract more developers and increase API adoption. - Revenue-sharing model is similar to SaaS marketplaces, with AWS taking a small cut. - AWS follows Google Cloud and Microsoft, who have also launched agent marketplaces.
Grok 4 Launch: Technical Advances, Pricing, and Safety Controversies
Grok 4, the latest LLM from xAI, debuted amid both technological hype and reputational crisis. Elon Musk’s live demo showcased Grok’s expanded capabilities, including a 256,000-token context window, multimodal input, and competitive benchmark scores. The model is now available via API and a new subscription model targeting both consumers and developers. Musk acknowledged the bots excessive compliance and promised improvements, but industry observers remain critical of the companys approach to prompt engineering and model governance. Despite these issues, xAI is pushing forward, promising further investments in video generation, voice capabilities, and future integrations with robotics. Key Points
- Grok 4 features a 256,000-token context window, image and text input, and API/subscription access.
- Benchmarks suggest Grok 4 outperforms peers like OpenAI o3 and Gemini 2.5 Pro, but transparency is lacking.
- Pricing is competitive, consumers can access Grok 4 via a new $30/month or $300/year “SuperGrok” plan - or a $300/month or $3,000/year “SuperGrok Heavy” plan providing access to Grok 4 Heavy.
- Recent prompt changes led to Grok 3 producing offensive content, exposing gaps in safety and oversight.
- xAI promises rapid iteration, new features, and a focus on “maximally truth-seeking” AI, but trust issues linger.
AI Showdown 2025: The Best AI Tools for Leaders and Developers 🤖
Dave’s Garage delivers a hands-on, comparative review of leading AI assistants—ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Grok—targeted at senior technical leaders and hardcore developers. By testing each with real-world scenarios, Dave highlights their unique strengths, contextual use cases, and critical limitations. The video underscores the rapid evolution of generative AI, with each tool excelling in distinct domains: ChatGPT for multimodal tasks and memory, Claude for developer collaboration and code quality, Gemini for massive context handling and integration, and Grok for real-time, uncensored search and reasoning. Dave also covers practical aspects like free vs. paid tiers, context window size, and integration with developer workflows. The review is grounded in direct experience and community feedback, offering actionable insights for C-suite executives and product managers seeking to future-proof their AI adoption strategies. The bottom line: No single AI is best for all needs—success depends on matching the right tool to the right workflow and business goal. Key Points:
- ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Grok each excel in specific AI scenarios; no universal winner.
- ChatGPT leads in multimodal capabilities and user memory; Claude is favored for code quality and collaborative problem-solving.
- Gemini offers unmatched context window size and seamless integration with Google’s ecosystem.
- Grok stands out for real-time search, reasoning, and minimal content filtering.
- Strategic AI adoption requires aligning tool capabilities with organizational needs and developer workflows.
How We Get to AGI: François Chollet’s Blueprint for Adaptive Intelligence 🚀
In his Y Combinator talk, François Chollet—creator of Keras and founder of the ARC Prize—delivers a compelling argument that scaling today’s deep learning models is not the path to artificial general intelligence (AGI). Instead, Chollet advocates for a paradigm shift: building AI systems that can adapt, reason compositionally, and invent solutions in novel contexts. He critiques the current focus on pretraining and memorization, highlighting the diminishing returns of brute-force scaling. Chollet introduces the ARC benchmark as a rigorous test for true generalization and abstraction, pushing the field beyond pattern recognition. He also discusses the 2024 shift toward test-time adaptation, the importance of compositional reasoning, and the need for meta-learning systems that fuse intuition with symbolic logic. Chollet’s new research lab, NDEA, is dedicated to pioneering these next-generation adaptive AI architectures. For senior leaders and technical teams, this talk is a call to rethink AI roadmaps: the future belongs to systems that can learn, adapt, and invent on the fly. Key Points
- Scaling Limits: Merely increasing model size and data yields diminishing returns; true AGI requires adaptive, generalizing systems.
- ARC Benchmark: Chollet’s ARC Prize sets a new standard for measuring abstraction and reasoning, not just memorization.
- Test-Time Adaptation: The field is shifting toward models that adapt in real time, moving beyond static pretraining.
- Compositional Reasoning: Next-gen AI must compose abstractions and invent solutions, mirroring human creativity.
- Meta-Learning & NDEA: Chollet’s NDEA lab is focused on meta-learning architectures that blend intuition with symbolic reasoning for robust, inventive intelligence.
Morgan Stanleys DevGen.AI: Modernizing Legacy Code at Scale
Morgan Stanley has internally developed and patented DevGen.AI, an AI-powered tool designed to automate the conversion of legacy code into modern programming languages. Launched in January 2025, DevGen.AI has already saved the banks developers over 280,000 hours by translating outdated code such as COBOL into plain-English specifications, streamlining modernization efforts across the firm. The tool was conceived during a hackathon and built by a small, agile team, later expanding to 20 engineers. Importantly, leadership emphasizes that DevGen.AI is intended to eliminate repetitive, rote tasks rather than reduce headcount. The bank continues to hire software engineers, highlighting that modernization demand far exceeds available technical resources. DevGen.AI remains an internal asset for now, with no immediate plans for external licensing, despite its high potential value to other organizations facing similar legacy code challenges. The projects success also underscores Morgan Stanleys broader innovation culture, supported by initiatives like the Patent Accelerator Program, which has increased patent filings and fostered cross-functional collaboration.
Key Points:
- DevGen.AI has automated legacy code modernization, saving over 280,000 developer hours in six months.
- The tool was developed in-house by a small, focused team and is protected by a newly granted patent.
- Morgan Stanley leadership stresses that the tool eliminates repetitive work, not jobs; the firm is still hiring engineers.
- DevGen.AI will remain an internal solution for now, supporting the bank’s ongoing modernization needs.
- The Patent Accelerator Program has driven a culture of innovation, increasing patent activity across the firm.
✉️ Grammarly Acquires Superhuman: AI Writing Meets Elite Email
Grammarly scooped up Superhuman, not for its fast email UX—but for its AI bones. This isn’t about inboxes; it’s Grammarly betting big on full-stack communication intelligence. Superhuman’s autocomplete, summarization, and intent-aware features are primed to become Grammarly’s new muscle across docs, messages, and more. Expect the real play to be Grammarly morphing from grammar checker to AI comms co-pilot—enterprise-ready, context-rich, and vertically integrated.
Key Insights
- Grammarly acquires Superhuman for an undisclosed sum, targeting AI-first email tech.
- Superhuman’s models already autocomplete, summarize, and infer email intent.
- Grammarly aims to embed these capabilities into its broader communication suite.
- Both companies emphasize “clarity,” “speed,” and “intent”—expect tight product fusion.
- This signals Grammarly’s move beyond correction into AI-native writing orchestration.
Spegel: A LLM-Powered Terminal based Web Browser
Spegel proves that browsers can become mere IO adapters once LLMs own the rendering pipeline. By treating Gemini 2.5 Pro Lite as a real-time markup engine, Simondw rewinds the web back to text—but under your prompt’s control. It’s a weekend hack with rough edges (no POST, potential token costs) , yet the idea unlocks CLI dashboards, context-aware docs, and accessibility tweaks without touching site code.
Key Insights
- Spegel pipes raw HTML through Gemini 2.5 Pro Lite, rendering concise Markdown inside your terminal.
- Dynamic prompt-based “views”—ELI5, action-only, recipe-extract—adapt content on the fly.
- No JavaScript; GET-only fetches today, with POST forms on the roadmap.
- Textual-powered TUI streams complete lines to maintain Markdown stability.
- MIT-licensed on GitHub—fork it, tweak prompts, share views.
Building software with agents : Building a Personal AI factory
John Rush, the author, introduces his innovative workflow for software development. He employs a combination of multiple agents and Gift Work Trees to construct code, adhering to the principle of fixed inputs rather than outputs. His approach is particularly intriguing, as he utilizes multiple agents across various LLMs to accomplish his coding tasks. This begs the question: is this a novel method of software development, and are other developers working with agents using similar workflows? If you have used agents for developing software please comment on how you are using them.
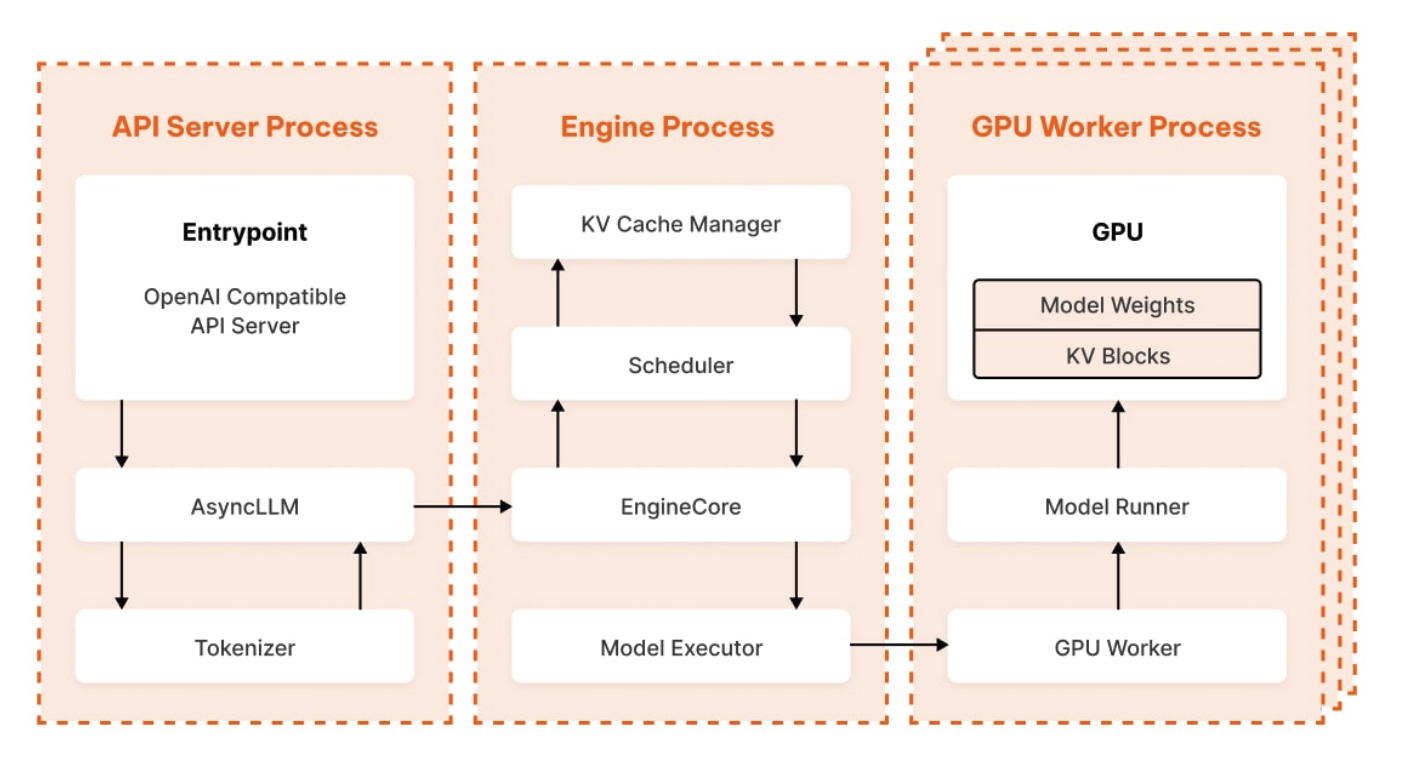
🚀 LLM Inference at Scale : High‑Throughput, Low‑Latency Architecture
Junhao Li’s write‑up masterfully dissects vLLM V1’s architecture—from HTTP request to GPU matrix ops—revealing how smart batching and paged KV cache transform LLM serving. This isn’t just academic elegance; it’s a hardcore systems‑level play, marrying OS-style memory paging with GPU scheduling for win‑win efficiency. Contrasting with monolithic inference loops, vLLM’s modular flow (API → Async LLM → EngineCore → GPU → back) sidesteps Python’s Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) hits and scales predictably. For engineering teams building inference platforms, the punchline is clear: combine continuous batching, cache paging, and IPC-driven parallelism to crush latency and cost simultaneously.
Life of an Inference Request (vLLM V1): How LLMs Are Served Efficiently at Scale
H20 Drought Stalls DeepSeek’s R2 Ambitions
DeepSeek’s hiccup highlights a brutal truth: algorithmic breakthroughs are hostage to chip geopolitics. By stranding H20 shipments, Washington throttles China’s flagship LLM contender and showcases CUDA lock-in as strategic leverage. Unless DeepSeek re-platforms on domestic Ascend or AMD’s export-compliant silicon, R2 risks debuting after leaner, MoE-powered rivals capture mindshare. In 2025, hardware independence—not parameter count—decides who stays on the bleeding edge.
- US export curbs choke Nvidia H20 supply, freezing DeepSeek’s R2 training pipeline.
- R2 aims to outgun R1 but CEO Liang still rejects its performance.
- DeepSeek trained R1 on 50 K Hopper GPUs—30 K H20, 10 K H800, 10 K H100.
- Most R1 users rely on H20 hardware, now scarce, threatening deployments.
- Chinese cloud operators fear R2’s compute surge will overwhelm clusters.
- Export ban exposes China’s AI dependence on U.S. silicon and CUDA stack.
A clever hack by George Mandis - Cut Your OpenAI Transcription Costs in Half with This Simple Audio Hack
Want to cut costs on OpenAI’s audio transcription (gpt-4o) without sacrificing quality? George Mandis discovered a simple yet brilliant hack: speed up your audio with ffmpeg before uploading. Running files at 2x or 3x playback speed slashes the minutes (and dollars) charged, while maintaining near-identical transcript quality—ideal for webinars, interviews, and long recordings. Bonus: it also bypasses model limits that choke on longer real-time files. Smart, scrappy optimisation—exactly the kind of engineering mindset we need more of.